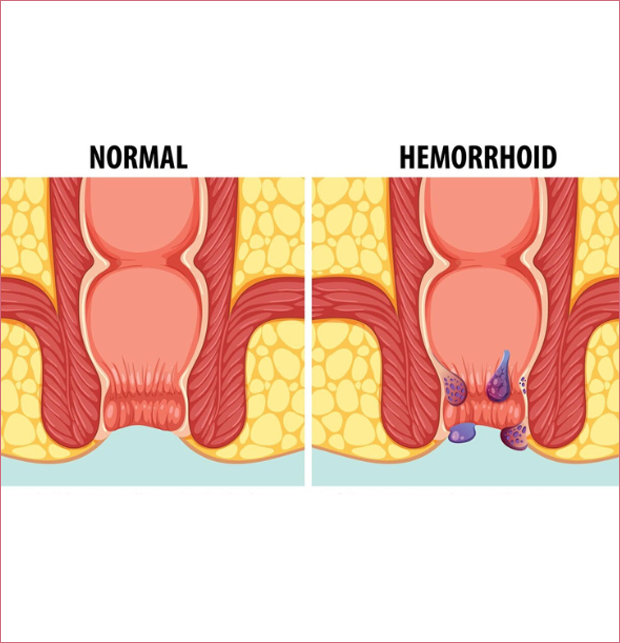
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids occur when veins in the lower rectum or anus become swollen, similar to varicose veins. This condition can lead to pain, discomfort, itching and bleeding, especially during bowel movements. Hemorrhoids are common and can affect both men and women, with the severity of the condition varying from mild to more serious cases.
Types of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are generally classified into two types based on their location:
-
Internal Hemorrhoids:
- Found inside the rectum and usually not visible.
- Cause painless bleeding during bowel movements.
- Can prolapse (bulge out) in advanced cases, causing pain and discomfort.
-
External Hemorrhoids:
- Found under the skin around the anus.
- May cause itching, swelling, pain, or bleeding if thrombosed (blood clot forms inside the hemorrhoid).
Grades of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are also graded based on their severity and how far they protrude from the anus. These grades are:
-
Grade 1:
- Internal hemorrhoids that don’t protrude outside the anus.
- May cause bleeding but no prolapse.
-
Grade 2:
- Internal hemorrhoids that prolapse during bowel movements but return on their own
- Can cause bleeding and discomfort.
-
Grade 3:
- Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids that don’t return on their own and require manual repositioning.
- Can cause significant pain and discomfort.
-
Grade 4:
- Severe internal hemorrhoids that are permanently prolapsed and can’t be pushed back.
- These may require surgical intervention due to pain and risk of blood clots.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Common hemorrhoid symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the anal region, especially when sitting or during bowel movements.
- Bleeding during bowel movements (bright red blood on toilet paper or in the stool).
- Itching or irritation around the anus.
- Swelling or lumps near the anus.
- Mucus discharge if the hemorrhoids are prolapsed.
Ignoring symptoms could lead to worsening discomfort, or complications like thrombosed hemorrhoids (clots forming in external hemorrhoids).
Causes and Risk Factors of Hemorrhoids
Key factors that contribute to the development of hemorrhoids include:
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
- Straining during bowel movements.
- Pregnancy: Increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic area.
- Obesity: Added pressure on the rectal veins.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity.
- Aging: Weakening of the tissue supporting the veins in the rectum.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
There are several treatment options available for hemorrhoids, ranging from at-home remedies to medical procedures.
-
Conservative Treatment:
- Fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation.
- Warm sitz baths for soothing the anal area.
- Over-the-counter creams and ointments to relieve itching and pain.
-
Minimally Invasive Treatments:
- Rubber band ligation: A small band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
- Infrared coagulation: Uses heat to shrink hemorrhoidal tissue.
-
Surgical Treatments:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal of large hemorrhoids
- Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: A less invasive surgery to reposition the hemorrhoid and remove excess tissue.
Why Choose Surgical Treatment for Hemorrhoids?
In cases where hemorrhoids are severe or don’t respond to other treatments, surgical removal may be necessary.
- Hemorrhoidectomy is highly effective in removing large or prolapsed hemorrhoids.
- Less recurrence: Surgical treatments offer long-term relief with a lower chance of hemorrhoids returning.
- Quick recovery with proper aftercare, minimizing future complications.






